Revealing the Six Big Losses in Lean Manufacturing: Paving the Path to Excellence
Table of Contents
Are you striving to make your manufacturing processes more efficient and your company world-class? If your answer is yes, then understanding and addressing the Six Big Losses in lean manufacturing, also known as Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE), is essential. In this article, we will take a friendly and informative journey through the concept of these six big losses, shedding light on why they matter and how they can help your organization achieve operational excellence.
The Six Big Losses: What Are They?
The Six Big Losses in lean manufacturing, as introduced by Seiichi Nakajima in 1971 while at the Japanese Institute of Plant Maintenance, are a set of crucial factors that can impact the efficiency of your manufacturing operations. These losses occur during routine manufacturing processes and can be the silent culprits behind wasted time, effort, and costs within your company.
Why Should You Care?
Imagine your manufacturing facility running at less than its full potential, hindered by avoidable losses. These losses lead to decreased profits, lower employee morale, and hinder your journey to becoming a world-class organization. The first step towards improvement is recognizing and understanding these losses. Only then can you take corrective actions to minimize or, in some cases, eliminate them from your system.
Unveiling the Six Big Losses
The concept of the Six Big Losses stems from Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) and is designed to break down the OEE factors—Availability, Performance, and Quality—further, allowing for a deeper analysis, prioritization, and minimization of losses. Each category of OEE factors have 2 types of losses each and we mentioned them in bold letters down.
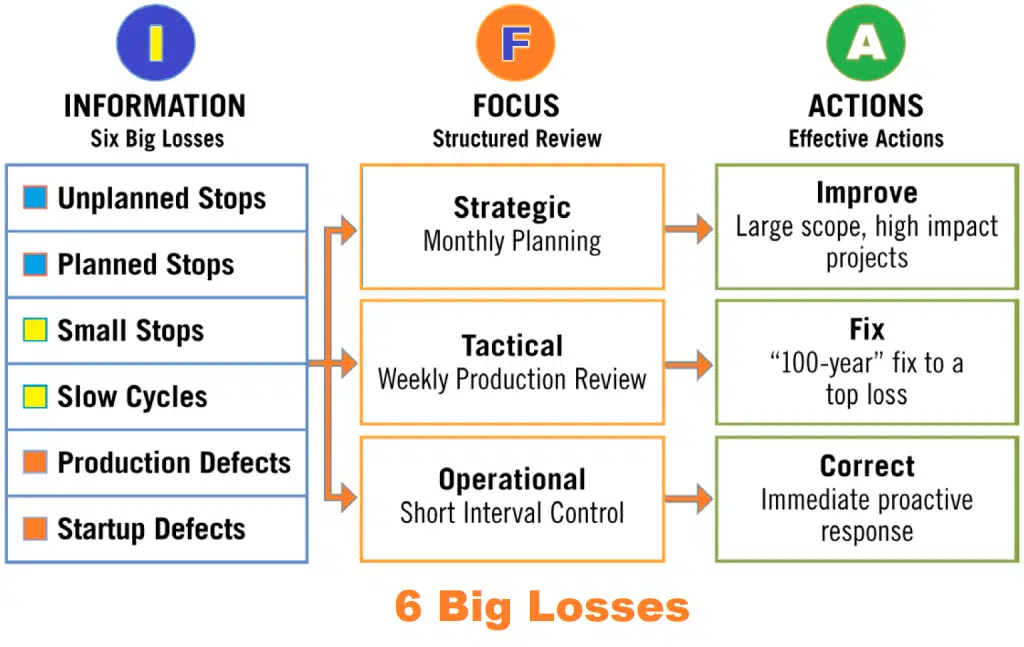
Losses in Availability
Availability losses can be categorized into two main types: (1) Planned Stops and (2) Unplanned Stops. Planned stops include activities like scheduled maintenance, operator training, breaks, changeovers, meetings, and inspections. Unplanned stops, on the other hand, result from equipment breakdowns, technical faults, material shortages, machine wear, electricity failures, or operator shortages.
How is Availability calculated in OEE?
Availability (%) = (Operating Time – Downtime) / Operating Time
Losses in Performance
Performance losses can be categorized into two main types: (1) Small/Minor Stops and (2) Slow/Reduced Cycles. Performance losses manifest in various forms, with speed being a significant factor. When a machine runs below 100% capacity or at a reduced speed, it indicates a performance loss. Causes can range from poor lubrication and low-quality materials to inexperienced operators and unfavorable environmental conditions. Additionally, small and frequent stops, such as machine jams or operator errors, contribute to performance losses.
How is Performance calculated in OEE?
Performance (%) = (Ideal Cycle Time / Actual Cycle Time) * 100
Losses in Quality
Quality losses can be categorized into two main types: (1) Production Defects and (2) Startup Defects.
Quality losses are associated with the production of defective parts, which can be classified as scrap or rework. Scrap consists of parts that are irreparable and must be discarded, while rework involves defective parts that can be rectified and reintroduced as good parts. Quality is measured as the percentage of good parts produced compared to the total parts produced.
So the three broad categories of losses contain the total of (3×2) = 6 Big Losses under them.
How is Quality calculated in OEE?
Quality (%) = (Good Count / Total Count) * 100
Striving for World-Class OEE
In an ideal world, achieving a perfect OEE score of 100% would be the goal. However, practicality dictates otherwise. Typically, companies aim for availability around 85-90%, performance ranging from 90-95%, and quality at approximately 80-85%. Combining these factors, a world-class company can achieve an OEE score of around 85%.
What is the formula for calculating overall OEE?
OEE (%) = Availability (%) * Performance (%) * Quality (%)
Putting Theory into Practice
To illustrate how these losses are calculated, let’s consider an example. Suppose you have an 8-hour shift, two 15-minute short breaks, one 50-minute meal break, 60 minutes of downtime, and an idle run/cycle time of 60 pieces per minute. Your total production is 18,000 pieces, with 420 rejected pieces.
By applying the formulas discussed above, you can calculate losses in terms of availability, performance, and quality. These calculations will give you valuable insights into where your losses are occurring and how they impact your overall efficiency.
In conclusion, understanding and addressing the Six Big Losses in lean manufacturing is a crucial step towards achieving operational excellence. By identifying and mitigating these losses, your company can enhance efficiency, boost profitability, and move closer to becoming a world-class organization.
We hope you found this article informative and valuable. If you did, please consider subscribing, liking, and sharing it with your colleagues and friends on various social media platforms. Additionally, feel free to suggest topics or share your thoughts in the comments section below. Together, we can work towards a more efficient and productive future in manufacturing.
The Power of Corrective Action
Now that we’ve delved into the intricacies of the Six Big Losses, let’s explore how to turn this knowledge into meaningful action. Identifying these losses is just the first step; the real transformation happens when you take proactive measures to minimize or eliminate them.
Steps To Corrective Actions
Here are some practical steps you can take:
Scheduled Maintenance: Plan regular equipment maintenance during non-production hours to prevent unplanned downtime. A well-maintained machine is less likely to break down unexpectedly.
Operator Training: Invest in comprehensive training programs for your operators to ensure they have the skills needed to operate machinery efficiently and minimize errors.
Optimize Breaks: While breaks are essential, consider streamlining the break schedule to minimize production interruptions. Efficient breaks ensure your workforce stays refreshed without compromising productivity.
Efficient Changeovers: Work on reducing the time required for equipment changeovers. Quick and seamless transitions between product runs minimize idle time and boost overall performance.
Continuous Improvement: Encourage a culture of continuous improvement. Regularly review processes, gather feedback from your team, and implement changes that lead to efficiency gains.
Quality Control: Implement rigorous quality control measures to minimize scrap and rework. Identify root causes of defects and take steps to address them.
Performance Tracking: Use performance metrics and real-time monitoring systems to keep a close eye on machine performance. Early detection of issues allows for timely intervention.
Employee Engagement: Involve your employees in the improvement process. They often have valuable insights into how to optimize operations on the ground.
Technology Integration: Explore technological solutions, such as predictive maintenance and automation, to enhance efficiency and reduce losses.
The Path to Excellence
Understanding the Six Big Losses and taking steps to address them is a journey. It requires commitment, collaboration, and a willingness to embrace change. As you make progress in reducing these losses, you’ll likely see a positive impact on your bottom line, employee satisfaction, and your company’s reputation in the industry.
In the ever-evolving landscape of manufacturing, staying competitive means continually seeking ways to enhance your processes. The Six Big Losses framework provides a structured approach to identify and tackle inefficiencies, setting you on the path to operational excellence.
As you implement these strategies, remember that each organization is unique. Tailor your approach to your specific needs and goals, and be open to adapting as you learn and grow. With dedication and the right strategies in place, you can transform your manufacturing operations and move closer to achieving world-class status.
Conclusion
Thank you for taking the time to explore the world of lean manufacturing and the Six Big Losses. We hope this article has been informative and inspiring on your journey toward manufacturing excellence. If you have any questions or insights to share, please feel free to join the conversation in the comments section below. Together, we can shape a brighter future for manufacturing.




