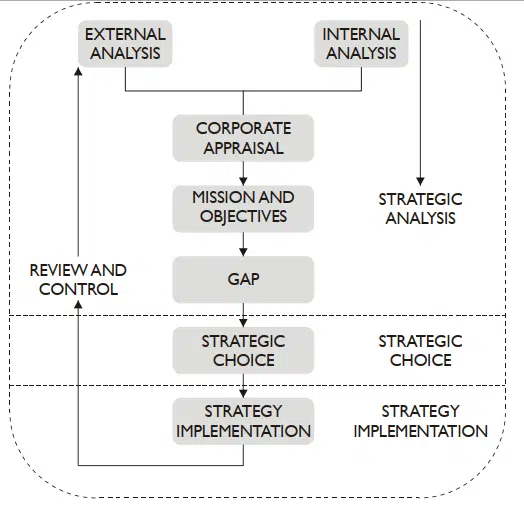
The rational planning approach sought to identify a process by which successful strategy can be formulated.
The main stages in the rational approach are:
- Conduct a corporate appraisal: This involves assessing the present business environment and assessing how it may develop over the timescale of the plan horizon (typically five + years). It will also consider the internal position of the business, including such things as its present staffing, quality of products and financial condition.
2. Set mission and objectives: Management will assess whether the long-term interests of the business are best met in its present industry and competing in its present way or whether the business needs to strike out in a new direction. This is called its mission. Objectives will be set for the coming years. The job of strategy is to attain them.
3. Gap analysis: Involves forecasting performance forward and comparing it with the strategic objectives set by management. If forecast performance is below the objectives set then this exposes a gap which must be filled by new and better strategy.
4. Strategic choice: Management must generate new business options for the firm such as new products or markets, and evaluate these to arrive at a set of potentially successful and affordable strategies to help the firm reach the objectives set.
5. Strategy implementation: Management carries out the strategy at corporate, business and functional levels by the development of organizational structures, policies and programmes to carry it out.